This post is also available in: Indonesia
Shortening and Emulsifier in Food Products in Japan
Shortening and emulsifiers are two endless topics to talk about in terms of its halal-ness in food products in Japan. These two ingredients are commonly compounded in the products, without any information whether it is derived from plants or animals, which makes us no other option than avoid doubtful things.
After a lot of inquiry came to us, we collect answers from Japanese food manufacturers about shortening and emulsifiers contained in their products for your reference. But first, let’s look closer at what kind of ingredient shortening and emulsifier are.
See Also
Identify Halal Products in Japan
Clearing Misconceptions in Food Ingredients
Shortening
Shortening is an odorless fat ingredient that is commonly used in bakery products such as cakes, bread, and biscuits to create soft texture on cakes and bread and crumbly texture on biscuits. It comes in a white cream-like texture at normal temperature, derived from both plants and animals.
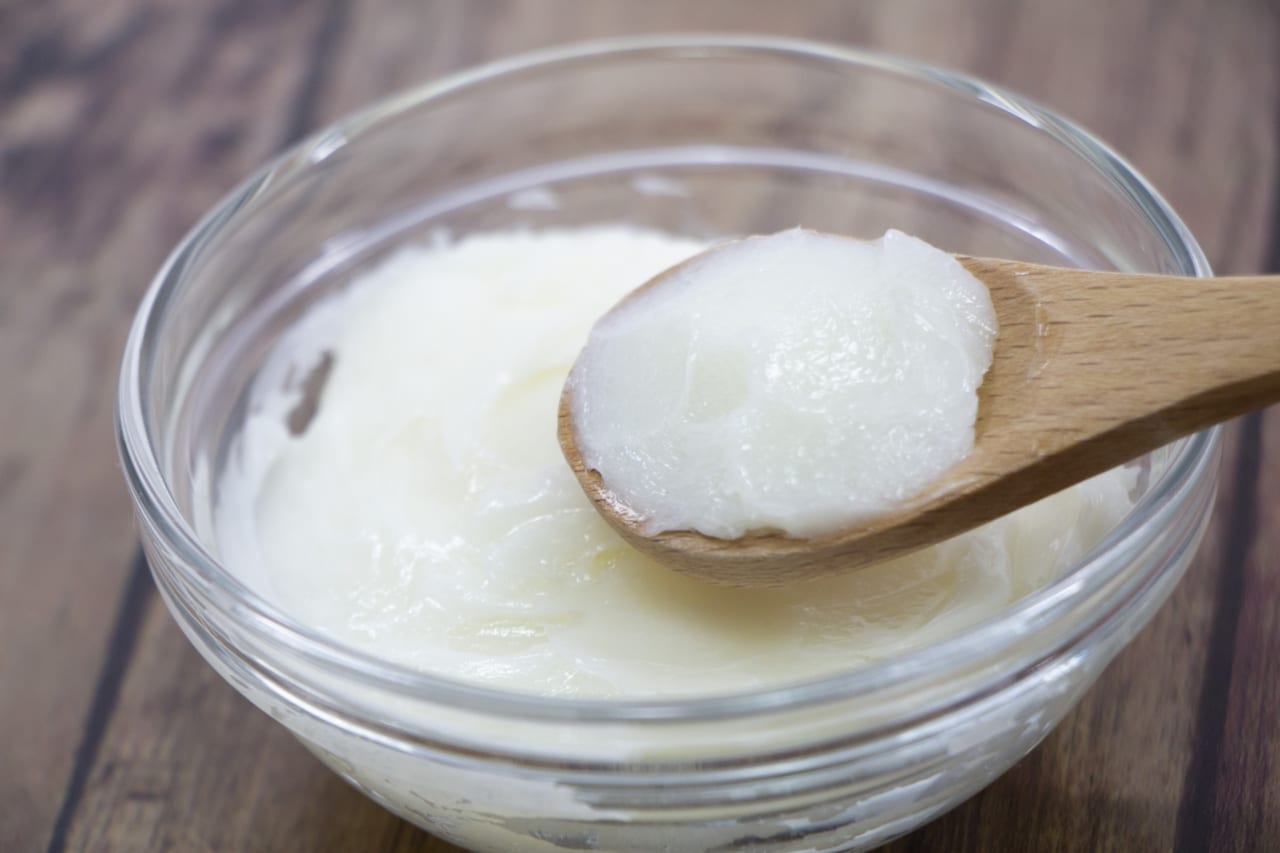

Shortening
According to Encyclopedia Mypedia (as quoted by Kotobank), shortening was considered as a substitute for lard in 1919, to deal with the lack of lard. It was made by mixing cottonseed oil with beef tallow. Later, with the invention of hydrogenated oil, hardened cottonseed oil and soybean oil were mainly used as raw materials, which became the basis of the current shortening. It is more stable to oxidation than ordinary vegetable oils, so it can be used widely.
Emulsifier
Emulsifier is an additive used to mix oil and water and emulsify them (turns them into a milky or creamy form) uniformly, using mainly lecithin (soybean), sucrose fatty acid ester, glycerin fatty acid ester, etc.

Emulsifier. Source: Madokawindow
According to Food Allergy, egg yolk and soybean are materials to make emulsifiers. If it is mentioned “lecithin (egg-derived)”, it means that the product contains eggs. However, eggs are not used if it is mentioned “lecithin (soybean derived)” or “lecithin” only.
Furthermore, Food Allergy mentions that 21 allergen items are considered as “equivalent to specific raw materials” and recommended to be labeled as much as possible. That’s why in some products you may find “emulsifier (soy-derived)” to prevent those with soy allergies from consuming.
See Also
Halal Certification and Muslim-Friendly Concept in Japan
Some answers from Japanese food companies’ FAQ
Data per 11 January 2022. Subject to change without notice.
Nissin Foods
One of the largest food companies, Nissin Foods described the origin of shortening in their cereals and snacks products as follows.

Source: Nissin FAQ
Q: Is shortening used in cereals and snacks plant-derived? or animal-derived?
A: The shortening used by Nissin is made from vegetable oil and fats that are mainly from palm oil. However, some of the emulsifiers used for shortening use raw materials derived from distilled animals (lard) (because they are distilled raw materials, they do not contain allergen proteins).
Furthermore, regarding emulsifiers, they mention as follows.

Source: Nissin FAQ
Q: Is emulsifier used in cereals and snacks are plant-derived? or animal-derived?
A: Lecithin used is derived from soy. Some part of shortening emulsifiers uses distilled animal (lard) derived ingredients.
Ishiya Co., Ltd
Meanwhile, Ishiya Co., Ltd who produces the popular Hokkaido snack, Shiroi Koibito answers as follows.
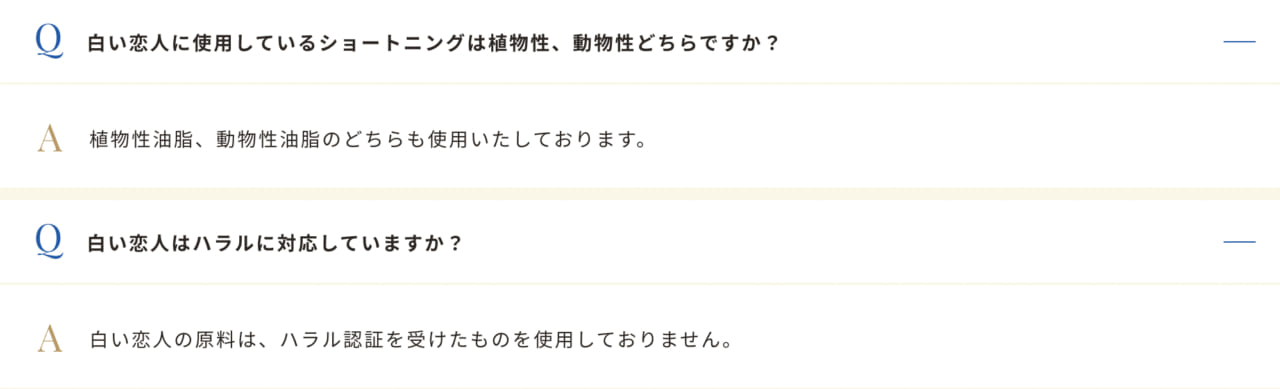
Source: Ishiya FAQ
Q: Is the shortening used for Shiroi Koibito plant-based or animal-based?
A: We use both vegetable fats and oils and animal fats and oils.
Q: Is Shiroi Koibito halal?
A: The raw materials used for Shiroi Koibito are not halal certified.
Ishiya Co., Ltd does not mention anything about emulsifiers. In some cases, you may find soy-derived emulsifiers written on the back pack of the product.
Bourbon Corporation
The company that is well-known for its choco-biscuit Alfort answers the question on their website as follows.
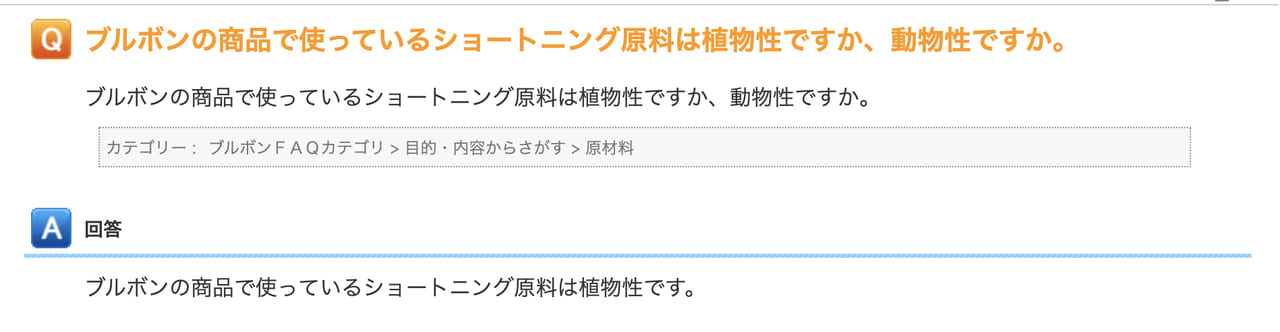
Source: Bourbon Corporation FAQ
Q: Is the shortening used for Bourbon products plant-based or animal-based?
A: Bourbon products use plant-based shortening.
However, they do not mention the emulsifiers used.
So, Can We Consume Shortening and Emulsifier?
One of the signs whether it is consumable or not is, the label of “plant-derived”. This label is extremely important for not only Muslims but also those with allergies as well as vegetarians and vegans.
According to the description above, shortening was mainly made from animals in the old days, while both plant-derived and animal-derived are commonly used these days. There is a possibility to use both (mixing the plant and animal-derived) in some cases. Meanwhile, the emulsifier is mainly made from plant-derived material. So that, it might be safer to avoid products with shortenings.
If you would like to have a product that you are conscious or concerned about, it will be safer to inquire to the manufacturing company for more detailed information or check the FAQ page on their official website.
*This article is describing the ingredients/materials. Note that there might be any contamination during the manufacturing process. Please directly inquire to each company for more info.
See Also
Is Mirin Halal? All About This Japanese Traditional Seasoning
Is Shoyu (Soy Sauce) Halal? Variety of Halal Shoyu in Japan
Any Halal Certified Miso in Japan?


